E-Invoice System User Manual for Tax Payers: NIC
Table of Contents
E-Invoice System User Manual for Tax Payers
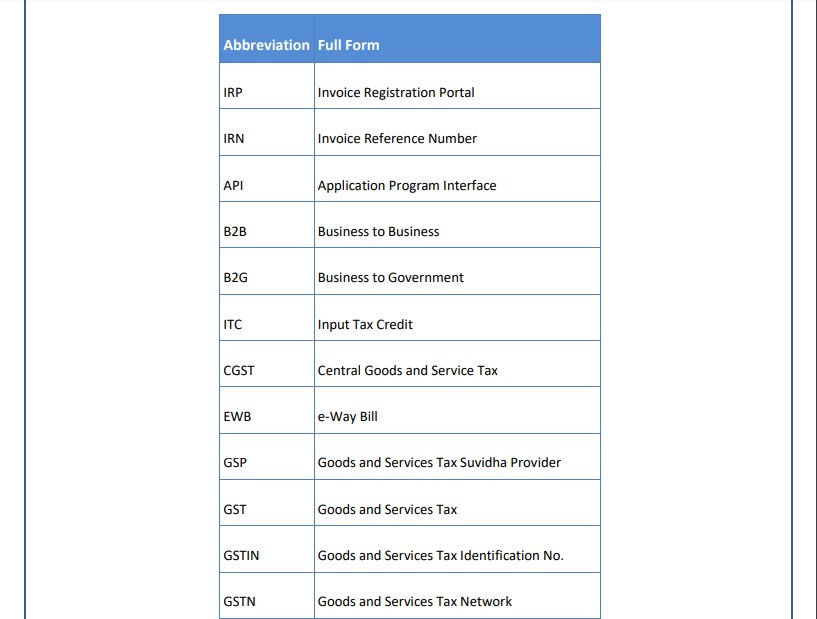
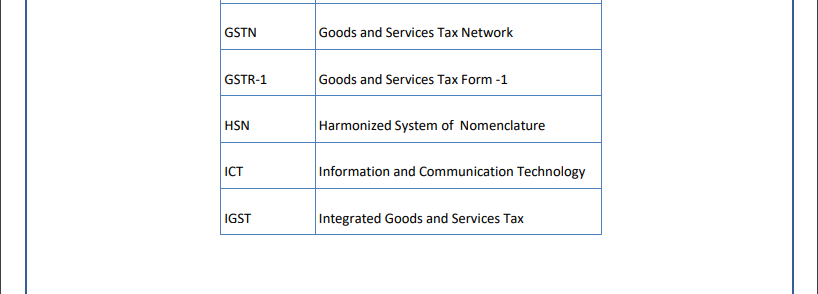
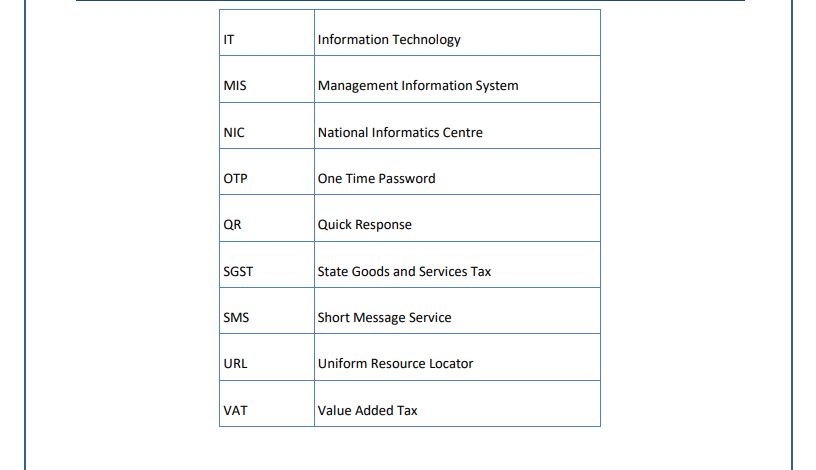
List of Abbreviations
1. Introduction
1.1 Background
The GST Council has approved the introduction of ‘E-invoicing’ or ‘electronic invoicing’ in a phased manner for reporting of business to business (B2B) invoices to GST System, starting from 1st January 2020 on a voluntary basis.
Since there was no standard for e-invoice existing in the country, a standard for the same has been finalized after consultation with trade/industry bodies as well as ICAI after keeping the draft in public place. Having a standard is a must to ensure complete interoperability of e-invoices across the entire GST eco-system so that e-invoices generated by one software can be read by any other software, thereby eliminating the need for fresh data entry – which is a norm and standard expectation today. The machine readability and uniform interpretation is the key objective. This is also important for reporting the details to the GST System as part of Return. Apart from the GST System, adoption of a standard will also ensure that an e-invoice shared by a seller with his buyer or bank or agent or any other player in the whole business eco-system can be read by machines and obviate and hence eliminate data entry errors.
The GST Council approved the standard of e-invoice in its 37th meeting held on 20th Sept 2019 and the same along with schema has been published on the GST portal. Standards are generally abstruse and thus an explanation document is required to present the same in common man’s language. Also, there is a lot of myth or misconception about e-Invoice. The present document is an attempt to explain the concept of e-invoice, how it operates and basics of standards.
E-invoicing in India will be a big move, due to the volume of business transactions undertaken every day, as well as the plethora of different, non-standardized formats used in invoice generation. The main objective is to enable interoperability across the entire GST eco-system i.e. an e-invoice generated by one software should be capable of being read by any other software. Basically, through machine readability, an invoice can be uniformly-interpreted.
In addition to the above, this new system of e-invoicing aims to make invoice reporting an integral part of a business process and remove the tedious task of invoice-compilation at the end of a return period. Claiming fictitious Input Tax Credit (ITC) by raising fake invoices is also one of the biggest challenges currently faced by tax authorities.
The e-invoice system will help to curb the actions of unscrupulous taxpayers and reduce the number of fraud cases as the tax authorities will have access to data in real-time. The basic aim behind the adoption of the e-invoice system by tax departments is the ability to pre-populate the return and to reduce the reconciliation problems.
1.2 Purpose and Intended Audience
This document aims to explain the operational procedure on how to use offline and online tools to generate e-invoices. This document is intended for registered taxpayers under GST, who are the main stakeholders of the e-invoice system under GST.
The present document is an attempt to explain the concept of e-invoice, how it operates and the basics of standards. It is expected that the document will be useful for the taxpayers, tax consultants and software companies to adopt the designed standard.
1.3 Scope
The scope of this document covers:
• Explaining the features of the e-invoice system.
• Activities of various stakeholders.
• Registration for the e-invoice system.
• Processes involved in the generation of web-based e-invoices.
• Enabling the various modes of the e-invoice generation.
• Managing the sub-users by the stakeholders.
• Using an online tool to generate e-invoices
• Process of uploading the generation of e-invoices.
1.4 URL or Web site address
IRP PORTAL
2. E-Invoice System
2.1 What is E-invoice?
If an invoice is generated by software on the computer or a machine then does it become an e-invoice? Is e-invoice as a system where taxpayers can generate the invoices centrally? Many such questions are raised when e-invoice gets discussed.
E-invoice does not mean the generation of invoices from a central portal of the tax department, as any such centralization will bring unnecessary restrictions on the way trade is conducted. In fact, taxpayers have different requirements and expectations, which can’t be met from one software generating e-invoices from a portal for the whole country. Invoice generated by every software may look more or less same; however, they can’t be understood by another computer system even though business users understand them fully. There are hundreds of accounting/billing software that generate invoices but they all use their own formats to store information electronically and data on such invoices can’t be understood by the GST System if reported in their respective formats.
Hence a need was felt to standardize the format in which electronic data of an Invoice will be shared with others to ensure there is interoperability of the data. The adoption of standards will in no way impact the way the user would see the physical (printed) invoice or electronic (ex pdf version) invoice. All these software would adopt the new e-Invoice standard wherein they would re-align their data access and retrieval in the standard format. However, users of the software would not find any change since they would continue to see the physical or electronic (PDF/Excel) output of the invoices in the same manner as it existed before the incorporation of e-Invoice standard in the software. Thus the taxpayer would continue to use his accounting system/ERP or excel based tools or any such tool for creating the electronic invoice as she is using today.
A taxpayer can enter the invoice details in bulk generation tool available on the e-invoice portal which in turn will create JSON file for uploading on the e-invoice system.
2.2 E-Invoice and Tax Department
The e-invoice system being implemented by tax departments across the globe consists of two important parts namely,
a) Generation of invoice in a standard format so that invoice generated on one system can be read by another system.
b) Reporting of e-invoice to a central system.
The basic aim behind the adoption of the e-invoice system by tax departments is the ability to pre-populate the return and to reduce the reconciliation problems. A huge increase in technology sophistication, increased penetration of Internet along with the availability of computer systems at a reasonable cost has made this journey possible and hence more than 60 countries are in the process of adopting the e-invoice.
GST Council has given the responsibility to design the standard of e-invoice and update the same from time to time to GSTN which is the custodian of Returns and invoices contained in the same. Adoption of e-invoice by GST System is not only part of Tax reform but also a Business reform as it makes the e-invoices completely inter-operable eliminating transcription and other errors.
Download the copy:
 ConsultEase Administrator
ConsultEase Administrator
Consultant
Faridabad, India
As a Consultease Administrator, I'm responsible for the smooth administration of our portal. Reach out to me in case you need help.








