GST Insights – New Year Amendments
Table of Contents
- GST Insights – New Year Amendments
- I. Amendments effective from 22nd December 2020
- A. Revision in time limits for granting GST registration
- B. Additional Grounds for Cancellation of GSTIN
- C. Suspension of registration without an opportunity of personal hearing
- D. Restrictions on filing GSTR-1 in case of non-filing of GSTR-3B
- E. Blocking of E-Way Bill Portal in case of suspension of GST registration
- II. Amendments effective from 1st January 2021
- F. Restriction on availment of ITC up to 105% as per Rule 36(4)
- G. Mandatory 1% payment of GST by Cash ledger for specified taxpayers
- H. E-way bill validity of single day for every 200 km instead of 100 Km
- III. Amendments are effective from a date to be notified later
- I. Stringent process for taking new registration
GST Insights – New Year Amendments
The Central Government has made critical amendments to CGST Rules, 2017 vide Notification No. 94/2020–Central Tax dated 22.12.2020 to make provisions more stringent and harsh for the businesses especially to curb tax evasion and ITC frauds.
I. Amendments effective from 22nd December 2020
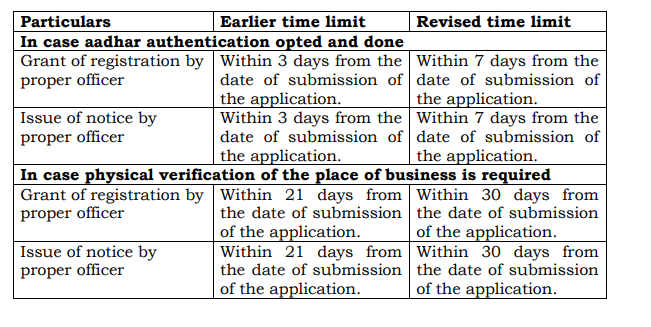
A. Revision in time limits for granting GST registration
Amendments in Rule 9 of CGST Rules, 2017 are summarized below:
B. Additional Grounds for Cancellation of GSTIN
The following additional grounds have been inserted under Rule 21 for cancellation of GST registration of taxpayers:
- Where a taxpayer avails ITC in violation of Section 16 of the Act i.e. ITC without bill/receipt of supply, violation of Section 16(4), nonpayment of tax by Supplier, non-business use, etc.
- Where the liability declared in GSTR-3B is less than that declared in GSTR-1 in a particular tax period.
- Violates the provision of rule 86B i.e., restrictions on the use of amount available in electronic credit ledger.
Our Comments: The cancellation of GST registration not only disrupts the business of the taxpayer and virtually bring business to a standstill but hinders the flow of the revenue of the Government as well. Cancellation merely on the basis of difference in GSTR-1 and GSTR-3B is draconian as there may be many reasons for the difference in GST returns. It should be ensured by the business that GSTR-1 and GSTR-3B should be reconciled for each tax period. Even in case of genuine difference for e.g. amendments made in GSTR-1 or adjustments of excess tax payments made in GSTR-3B, we may now expect Notices at ground level.
C. Suspension of registration without an opportunity of personal hearing
Various amendments in Rule 21A of CGST Rules, 2017 has been made, summarized below:
- The proper officer has been empowered to suspend GST registration without giving an opportunity of being heard to the taxpayer, where the proper officer has reasons to believe that the registration of a person is liable to be cancelled u/s 29 or Rule 21.
- In case of significant differences or anomalies between details of an outward supply in GSTR-3B vs GSTR-1 or ITC details in GSTR-3B vs GSTR-2B/2A, the department shall suspend the registration and serve a notice in FORM GST REG-31 to call explanation as to why GSTIN should not be cancelled within 30 days.
- No refund u/s 54 of CGST Act 2017 can be availed by the taxpayer in case of suspension of registration.
- It should be noted that in case of suspension of GSTIN, a taxpayer shall not issue a tax invoice during the period of suspension and shall not be required to furnish any return under section 39.
Our Comments: It is a settled principle of natural justice that any adverse action warrants the opportunity of personal hearing. The term ‘anomaly’ used in the amended Rule itself suggests oversight or a genuine mistake. The suspension of GST registration for ‘anomalies’ raises questions on the legal sanctity of the provisions.
D. Restrictions on filing GSTR-1 in case of non-filing of GSTR-3B
Rule 59(5) has been inserted to restrict the filing of GSTR-1 as under:
- For monthly return filers – Taxpayer failing to file GSTR-3B for the preceding 2 months shall not be permitted to file GSTR-1. Let’s say if GSTR-3B has not been filed for September and October 2020, GSTR1 cannot be filed for November 2020 onwards
- For quarterly return filers – Taxpayer failing to file GSTR-3B for the preceding quarter shall not be permitted to file GSTR-1 or IFF. Let’s say if GSTR-3B has not been filed for quarter Jan 21 to March 21, GSTR-1 cannot be filed for April to June 2021 quarter onwards
- A taxpayer who is restricted to utilize ITC for tax payments as per Rule 86B shall not be permitted to file GSTR-1 or IFF if GSTR-3B for the preceding tax period is not filed.
E. Blocking of E-Way Bill Portal in case of suspension of GST registration
An Amendment has been made in Rule 138E to provide that E-way bill portal shall be blocked for a taxpayer whose registration has been suspended under the provisions of Rule 21A(1)/(2)/(2A).
II. Amendments effective from 1st January 2021
F. Restriction on availment of ITC up to 105% as per Rule 36(4)
With effect from 01.01.2021, ITC on invoices/debit notes not furnished by suppliers in Form GSTR-1 or Invoice Furnishing Facility (IFF) now can be claimed up to 5% of the eligible credit as compared to earlier limit of 10%.
G. Mandatory 1% payment of GST by Cash ledger for specified taxpayers
The overriding Rule 86B has been inserted to the effect that in cases where the value of taxable supplies other than exempt supply and zero-rated supply exceeds Rs. 50 lakhs in a month, these taxpayers cannot use ITC of more than 99% to discharge the total tax liability and balance 1% is mandatory to be paid by using cash ledger.
Exceptions: The said restriction shall not apply where
i) The said person or the Proprietor or Karta or the Managing Director or any of its two Partners, Whole-time Directors, Members of Managing Committee of Associations or Board of Trustees, as the case may be, has paid Income Tax exceeding Rs. 1 lakh in last two financial years for which time to file ITR has been expired, that is, F.Y. 2018-19 and 2019-20
ii) Where the registered person has received a refund exceeding Rs. 1 lakhs of unutilized ITC on account of zero-rated supplies or inverted duty structure.
iii) Where the taxpayer has discharged his tax liability by using cash in excess of 1% of the total liability up to the said month in the current F.Y.
iv) Where a person is a Government Department, Public Sector Undertaking (PSU), local authority or a statutory body.
Note: To simplify, the restriction of 1% payment of GST in cash shall be seen on a cumulative basis in every Financial Year.
Further, the Commissioner has been empowered to remove the said restriction after verification and safeguards. It is still not clear how the provision will be operationalized.
Our comments: The profile and payment under Income tax cannot decide the genuineness of the assessee. The exclusion of PSU, Government Department, local authority or statutory body from the restriction of 1% is discriminatory in nature as the restriction applies to all private taxpayers (genuine or non-genuine) which may see a batch of writ petitions in High Court.
Related Topic:
GST Insights- Compliances before 31st March 21 and Changes w.e.f. 1st April 2021
H. E-way bill validity of single day for every 200 km instead of 100 Km
After generation of the e-way bill, the taxpayers shall cover a distance up to 200 kms in a single day which was earlier 100 Kms, i.e., earlier 2 days were given to cover the distance of 200 km which has now been reduced to 1 day.
III. Amendments are effective from a date to be notified later
I. Stringent process for taking new registration
While applying for new GST registration, w.e.f. 21.08.2020, Aadhar authentication of Proprietor/ Karta/ Managing Partners/ Authorised Signatory is required to be done if registration is to be obtained without prior physical verification of the business place.
Now, additional requirements would be required to be fulfilled to complete the registration process as under (except who are exempted under Section 25(6D) of CGST Act, 2017):
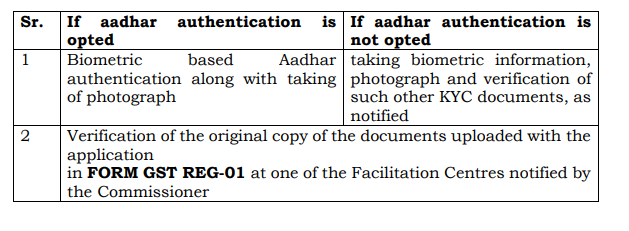
Our Comments: In the era of digitalization, submission of documents at the facilitation centers is a very old school and regressive step and will bring hurdles in doing business and we are back to the VAT era.
Disclaimer: The information in this document is for educational purposes only and nothing conveyed or provided should be considered as legal, accounting, or tax advice.
 CA Nikhil M Jhanwar
CA Nikhil M Jhanwar
Nikhil M Jhanwar is a practicing Chartered Accountant based in North India having a vast experience of 8 years in taxation advisory/compliances, litigation support, drafting replies to Show Cause Notices, and representing clients before the Department in Indian GST and UAE VAT. He has closely worked on GST implementation in India and UAE VAT implementation in particular impact analysis, regulatory support, implementation support, I.T. support, tax advisory, and compliances. Being a Faculty Member of GST by ICAI, he regularly speaks at forums and seminars on various topics of GST. He is a keen writer and his articles have been published in prominent tax journals and websites.









