FAQs on GST e-invoice/IRN System
Table of Contents
- A. E-invoice – Basics:
- 1. What is ‘e-invoicing’?
- 2. How is ‘e-invoicing’ different from the present system?
- 3. For which businesses, e-invoicing is mandatory?
- 4. What are the advantages of e-invoice for businesses?
- 5. What businesses need to do, to be e-invoice ready?
- 6. Is an invoice/CDN/DBN (required to be reported to IRP by notified person), valid without IRN?
- B. E-invoice – Applicability:
- 7. What documents are presently covered under e-invoicing?
- Read & Download the full copy in pdf:
A. E-invoice – Basics:
1. What is ‘e-invoicing’?
As per Rule 48(4) of CGST Rules, notified class of registered persons has to prepare the invoice by uploading specified particulars of the invoice (in FORM GST INV-01) on Invoice Registration Portal (IRP) and obtain an Invoice Reference Number (IRN).
After following the above ‘e-invoicing’ process, the invoice copy containing inter alia, the IRN (with QR Code) issued by the notified supplier to a buyer is commonly referred to as ‘e-invoice’ in GST.
Because of the standard e-invoice schema (INV-01), ‘e-invoicing’ facilitates the exchange of the invoice document (structured invoice data) between a supplier and a buyer in an integrated electronic format.
Please note that ‘e-invoice’ in ‘e-invoicing’ doesn’t mean the generation of invoices by a Government portal.
2. How is ‘e-invoicing’ different from the present system?
There is no much difference indeed.
Registered persons will continue to create their GST invoices on their own Accounting/Billing/ERP Systems. These invoices will now be reported to ‘Invoice Registration Portal (IRP)’. On reporting, IRP returns the e-invoice with a unique
‘Invoice Reference Number (IRN)’ after digitally signing the e-invoice and adding a QR Code. Then, the invoice can be issued to the receiver (along with QR Code)
A GST invoice will be valid only with a valid IRN.
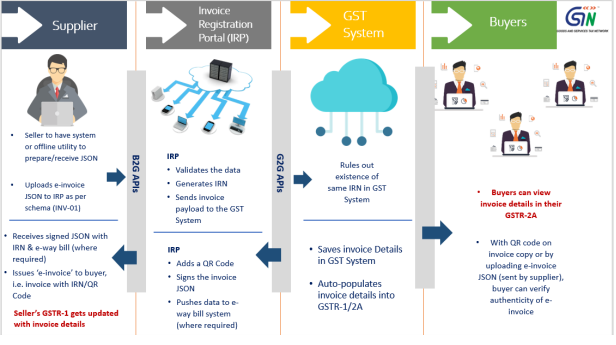
For a more detailed process, please go through ‘e-invoice – Detailed Overview’
3. For which businesses, e-invoicing is mandatory?
For Registered persons whose aggregate turnover (based on PAN) in any preceding financial year from 2017-18 onwards, is more than the prescribed limit (as per relevant notification), e-invoicing is mandatory.
4. What are the advantages of e-invoice for businesses?
e-invoice has many advantages for businesses such as Auto-reporting of invoices into GST return, auto-generation of the e-way bill (where required).
e-invoicing will also facilitate standardization and interoperability leading to reduction of disputes among transacting parties, improve payment cycles, reduction of processing costs, and thereby greatly improving overall business efficiency.
5. What businesses need to do, to be e-invoice ready?
Businesses will continue to issue invoices as they are doing now. Necessary changes on account of e-invoicing requirement (i.e. to enable reporting of invoices to IRP and obtain IRN), will be made by ERP/Accounting and Billing Software providers in their respective software. They need to get the updated version having this facility.
6. Is an invoice/CDN/DBN (required to be reported to IRP by notified person), valid without IRN?
As per Rule 48(4), notified person has to prepare the invoice by uploading specified particulars in FORM GST INV-01 on Invoice Registration Portal and after obtaining the Invoice Reference Number (IRN).
As per Rule 48(5), any invoice issued by a notified person in any manner other than the manner specified in Rule 48(4), the same shall not be treated as an invoice.
So, the document issued by a notified person becomes legally valid only with an IRN.
B. E-invoice – Applicability:
7. What documents are presently covered under e-invoicing?
i. Invoices
ii. Credit Notes
iii. Debit Notes,
when issued by notified class of taxpayers (to registered persons (B2B) or for the purpose of Exports) are currently covered under e-invoice.
Though different documents are covered, for ease of reference and understanding, the system is referred to as ‘e-invoicing’.
Read & Download the full copy in pdf:
 ConsultEase Administrator
ConsultEase Administrator
Consultant
Faridabad, India
As a Consultease Administrator, I'm responsible for the smooth administration of our portal. Reach out to me in case you need help.








