E-invoicing – At a Glance
Table of Contents
What is e-invoicing?
As per Rule 48(4) of CGST Rules, notified class of registered persons (whose aggregate turnover in any preceding financial year from 2017-18 onwards, is more than prescribed limit) have to prepare invoice by uploading specified particulars of invoice (in FORM GST INV-01) on Invoice Registration Portal (IRP) and obtain an Invoice Reference Number (IRN).
After following the above ‘e-invoicing’ process, the invoice copy containing inter alia, the IRN (with QR Code) issued by the notified supplier to a buyer is commonly referred to as ‘e-invoice’.
As per Rule 48(5), any invoice issued by a notified person in any manner other than the manner specified in Rule 48(4), the same shall not be treated as an invoice.
A standard format for e-invoice was notified as ‘INV-01’. This format (called ‘schema’) facilitates seamless exchange of invoices between accounting systems of suppliers and buyers in an integrated electronic format.
Related Topic:
E-Invoice Schema Format – Mandatory Fields
E-invoicing – Procedure:
Nowadays, most businesses are using one or other Accounting/Billing/ERP Systems to create and manage their invoices. These invoices (in JSON format) will now be reported to ‘Invoice Registration Portal (IRP)’. IRP returns the digitally signed invoice (in JSON) with a unique ‘Invoice Reference Number (IRN)’ and a QR Code.
That means the Accounting/ERP system of business and e-invoice system of government will be ‘talking to each other for the exchange of invoice data. All this ‘machine-to-machine interaction through APIs and generation of IRN happens in a split second indeed.
Modes of API integration are as below:
Taxpayers with Aggregate Turnover of < Rs. 500 Crores
- Through E-Way Bill APIs – If the taxpayer already has direct access to E-Way Bill APIs, then they can use the same Client Id, Client Secret, username, and password to get access to the e-Invoice system.
- Through GSPs – the taxpayer can connect through GSPs. In this case, the GSTIN generates their own username and password, ties up with GSPs to get access to e-invoice APIs using the Client ID and Client Secret of GSPs.
- Through ERPs or BilliThrough GSPsng/Accounting Software Service Providers – the taxpayer can connect through select ERPs and Billing/Accounting Software Service Providers. In this case, the GSTIN generates their own username and password and ties up with ERPs or Billing/Accounting Software Service Providers, to get access to e-invoice APIs, using the Client ID and Client Secret of said providers.
- Through Entities having direct Access to APIs – If the taxpayer (e.g. certain automobile companies) has tie-up or using the ERP of the entity which has direct access to API, then they can access e-invoice APIs through that entity. In this case, the GSTIN generates its own username and password and gets access to e-invoice APIs, using a Client ID and Client Secret of the entity which has such access.
Taxpayers with Aggregate Turnover of > Rs. 500 Crores
In addition to the above modes, they will have direct access, as follows:
•Direct Access to API – They can get direct access to API to integrate with their ERP system. They need to whitelist their public IPs. In addition to the username and password to each GSTIN of the entity, the entity gets the Client ID and Client Secret to get access to e-invoice APIs.
Some businesses may not have their own ERP/Accounting Software or have few invoices to report. They can download the free offline utility (‘bulk generation tool’) from the e-invoice portal. Using this, invoice data can be easily uploaded on IRP for the generation of IRN. While the portal gives back ‘machine-readable’ invoices in JSON format, there is a facility to generate ‘human-readable PDF copy of the invoice (for save/print/e-mail, etc.).
After obtaining IRN, the invoice (with QR Code) can be issued to the recipient in the same way as is being done now. (Note: An integrated mechanism to enable system-to-system exchange of e-invoices will be made available in due course.)
The detailed flow involved in e-invoicing is depicted below:
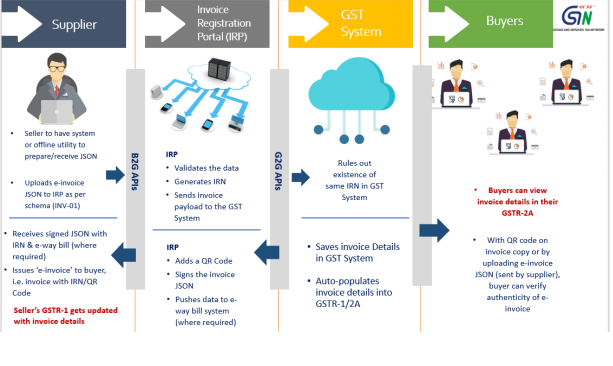
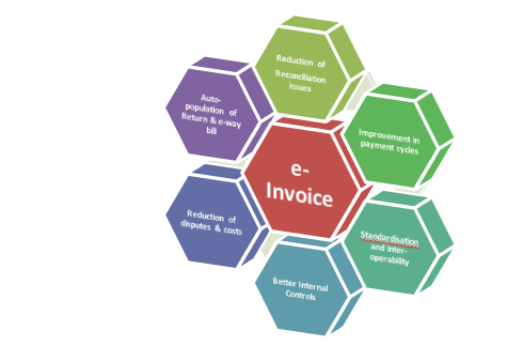
Advantages:
There are many advantages e-invoice brings in for businesses, as depicted below:
Documents/Supplies Covered:
| Documents covered | Supplies Covered |
| Invoices
Credit Notes Debit Notes |
Supplies to registered persons (B2B)
Supplies to SEZs (with/without payment) Exports (with/without payment) Deemed Exports Note: B2C invoices are not covered currently |
Read & Download the full copy in pdf:
Read & Download the Hindi version in pdf:
 ConsultEase Administrator
ConsultEase Administrator
Consultant
Faridabad, India
As a Consultease Administrator, I'm responsible for the smooth administration of our portal. Reach out to me in case you need help.









