E-Invoicing – Legal Provisions & Implementation Challenges
Table of Contents
- E-Invoicing – Legal Provisions & Implementation Challenges
- Why E-Invoicing?
- E-Invoice or Electronic Invoicing
- Who is required to issue E-Invoices?
- Relevant Notifications / Rules
- Persons Exempted
- Which transactions are covered by E-Invoicing Rules?
- B2C QR Code
- What about B2C Transactions by taxpayers with turnover over Rs 500 Crore?
- Terms and Definitions
- Invoice Reference Number (IRN)
- Invoice Registration Portal (IRP)
- Read & Download the full Copy in pdf:
E-Invoicing – Legal Provisions & Implementation Challenges
Why E-Invoicing?
• Digital Invoices / Accounting is a metric in Ease of Doing Business Ranking of countries
➢ India’s ranking moved up from 77 to 63 in 2019
• Moving digital will standardize various processes, reduce data entry errors, save cost
➢ 96% Cost Saving; 80% Time-saving; 15 times efficiency improvement
• Better compliance by Taxpayers simplifies audits
E-Invoice or Electronic Invoicing
- No prior standard under GST or any other statute
- Having a standard is a must for interoperability across various players (Supplier, Recipient, E-Way Bill System, Return Filing, Government)
- Interoperability between software Eliminates the need for data entry
- Other players Banks, Wholesale retail chain
Who is required to issue E-Invoices?
- CT NN 61/2020: Taxpayers with an aggregate turnover in a financial year above Rs 500 Crore from Oct 1, 2020.
- CT NN 88/2020 Taxpayers with an aggregate turnover in a financial year above Rs 100 Crore from Jan 1, 2021
Relevant Notifications / Rules
- CGST Notification 68/2019
- Rule 48- Manner of issuing an invoice
→48(4) – FORM GST INV-1
→48(5) – Invoice other than the above is not valid
→48(6) – Multiple copies of an invoice not required
- CGST Notification 69/2019 – Notifies Common Portal
- CGST Notification 60/2020 – Specifies Schema/fields of INV-01
Related Topic:
Implementation of Labour Codes
Persons Exempted
Special Economic Zone (SEZ) Unit
Persons covered by CGST Rule 54 (Sub-rules (2), (3), (4), (4A)
• Insurer or a banking company or a financial institution, including NBFC Goods
• Transport Agency
• Passenger transportation service
• Admission to an exhibition of cinematograph films in multiplex screens
* Updated as per Notification 61/2020 -CT
Which transactions are covered by E-Invoicing Rules?
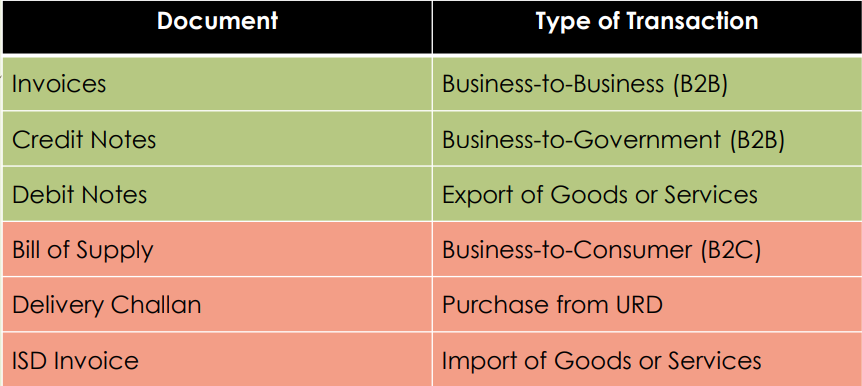
Applicable only for B2B Notification 70/2019
B2C QR Code
What about B2C Transactions by taxpayers with turnover over Rs 500 Crore?
Notification 72/2019
Not an E-Invoice, Requires digital payment QR Code
Terms and Definitions
Invoice Reference Number (IRN)
- Combines Taxpayer GSTIN, Financial Year, Document Type, Invoice Number
- 64-digit alphanumeric number to uniquely identify an Invoice
- For computers only, humans can ignore this
→GSTIN: 33AADCG4992P1Z0
→Financial Year: 2019-20
→Document Type: Invoice Document Number: 2
Invoice Registration Portal (IRP)
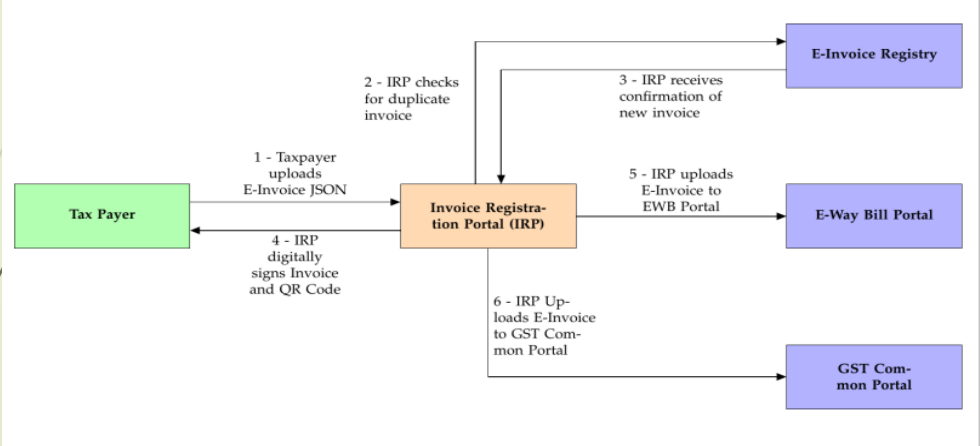
- Authorized by Government
→First IRP run by National Informatics Centre (NIC)
→Second IRP proposed to be run by Goods and Services Tax Network (GSTN)
- Verifies and acknowledges E-Invoices
- Replies within a blink of an eye
- Retains invoices for 24-hours
- Does not contain a listing of Invoices
Read & Download the full Copy in pdf:
 CA Venu Gopal Gella
CA Venu Gopal Gella
Keep learning
Banglore, India
GST









