FAQs on E Invoice under GST
Table of Contents
- 1. What is E invoicing?
- 2. When will E invoicing get implemented?
- 3. Who is required to raise the E invoice?
- 4. What if the invoice is not issued in terms of mentioned u/r 48(4) of CGST Rules, 2017?
- 5. How to generate an E invoice?
- 6. What are the myths about E invoicing?
- 7. Can we amend or cancel an E invoice?
- 8. What all are the immediate preparations required as an assessee?
- 9. Is there any facility of adding a discount amount at line item level?
- 10. Will it be possible for bulk uploading of E invoices?
- 11. What is Hash IRN under E invoice?
- 12. What will be the validity of the E invoice generated on the portal?
- 13. Will the E invoice schema cater to the reverse charge mechanism (RCM)?
- 14. Will there be an option for linking multiple invoices in case of debit/credit note?
- 15. Whether exports would require E invoice compliance? Also, does it allow the declaration of export invoices/zero rated supplies?
1. What is E invoicing?
Rule 48(4) has been inserted vide N/N 68/2019- CT dt 13.12.2019 which amends the rules w.r.t E invoicing.
‘E-invoicing’ or ‘electronic invoicing’ is a system in which B2B invoices are authenticated electronically by GSTN for further use on the common GST portal.
Under the proposed electronic invoicing system, an identification number will be issued against every invoice by the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP) to be managed by the GST Network(GSTN).
All invoice information will be transferred from this portal to both the GST portal and e-way bill portal in real-time.
Therefore, it will eliminate the need for manual data entry while filing GST returns as well as generation of part-A of the e-way bills, as the information is passed directly by the IRP to the GST portal.
2. When will E invoicing get implemented?
The electronic invoicing was to be mandatorily implemented from 1 April 2020 but has been pushed to 1st October 2020 for taxpayers with turnover over Rs 500 Crore. The aggregate turnover will include the turnover of all GSTINs under a single PAN, across India.
3. Who is required to raise the E invoice?
N/N 13/2020 – CT dt 21.03.2020 replaced with N/N 61/2020 dt 30.07.2020 provides that every registered person whose aggregate turnover in a financial year exceeds INR 500 crore, will be required to prepare an E invoice in terms of rule 48(4) of CGST Rules, 2017.
N/N 72/2019-CT dt 13.12.2019 replaced with N/N 14/2020- CT dt 21.03.2020 states invoice issued to an unregistered person whose aggregate turnover in a financial year exceeds INR 500 crores, is required to contain Quick Response Code (QR Code) to be generated.
4. What if the invoice is not issued in terms of mentioned u/r 48(4) of CGST Rules, 2017?
If an invoice does not accompany the terms prescribed under the said rule then such invoice shall be treated as invalid under GST.
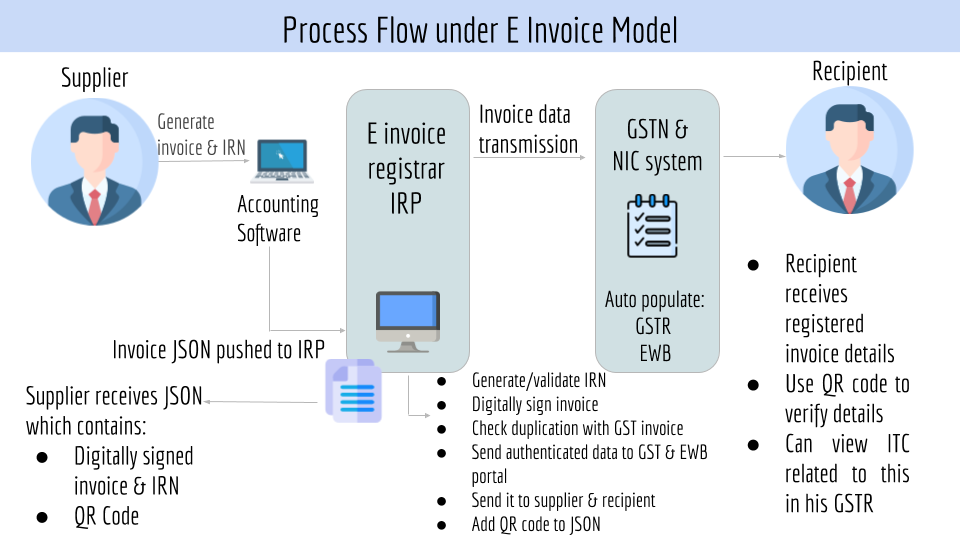
5. How to generate an E invoice?
Step by step process:
Step 1: Invoice Creation
The seller/supplier will create an invoice in the prescribed format (e-invoice schema) using his/her accounting or billing software. It must have the mandatory details.
The accounting software of the supplier will generate a JSON for each B2B invoice. The JSON file will be uploaded to the IRP.
Step 2: IRN Generation
The next step would be to generate a unique Invoice Reference Number (IRN) by the seller using a standard hash-generation algorithm.
Step 3: Invoice uploading
Now, the seller will upload JSON for each of the invoices, along with IRN, to the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP), either directly or through third-party software.
Step 4: Authentication and Signing
IRP will validate the IRN attached with JSON or generate an IRN if not already uploaded by the supplier.
Upon successful verification, it will add its signature on the invoice and a QR code to JSON.
Hash generated earlier will become the new IRN of the E-invoice. It will be the unique identity of that e-invoice for the entire financial year.
Step 5: Sharing of Data
The uploaded data will be shared with E way bill portal which will auto fill Part A. Respective GST return will also be auto populated.
Step 6: Availability to Recipient
Receiver will receive registered invoice details. He can use QR code to verify the details. He can also view the credit available to him in GSTR 2B.
6. What are the myths about E invoicing?
- E invoicing is to be generated on Common portal
- It’s a New / standard invoice format being designed now.
- It is only for invoice and not for debit/credit notes.
Correct views:
- E invoice is a system in which B2B invoices issued by suppliers are transmitted/ uploaded in Json file on an e portal notified government, which gets validated, digitally signed electronically by such e portal with unique generation of IRN and remitted to suppliers and recipient both for further use in various compliances such as preparation of GST returns, e way bill etc.
- E invoicing to be raised as per standard e invoice schema from your own Accounting, billing, ERP.
7. Can we amend or cancel an E invoice?
- E invoice cannot be partially cancelled. It has to be fully cancelled.
- Cancellation is to be done within 24 Hours on IRP.
- Any cancellation after 24 hours cannot be done on IRP, however one can manually cancel the same on GST portal before filing the returns.
- Amendments to the e invoice are allowed in GST portal only as per provisions of law.
8. What all are the immediate preparations required as an assessee?
- Invoices under the new E invoicing system will continue to be prepared using Existing software only.
- Such existing software must confirm to the prescribed standards and parameters.
- Your accounting software should be able to generate JSON files of the invoices uploaded.
9. Is there any facility of adding a discount amount at line item level?
Yes, E invoice has a provision of capturing discount at line item level. However it is to be maintained if applicable in that particular transaction.
10. Will it be possible for bulk uploading of E invoices?
Invoices have to be uploaded one at a time on IRP. The IRP will be able to handle a large sequence of invoices for registration and validate them. Bulk uploading will be required by large taxpayers, in such cases, their ERP or accounting software should be designed in such a way that it makes requests one by one.
11. What is Hash IRN under E invoice?
The hash function is a type of mathematical function, which, when applied to a digital file (record), assigns it a specific value called a hash.
The hash generated by IRP will become the IRN (Invoice Reference Number) of the E invoice. This shall be unique to each invoice and hence be the unique identity for each invoice for the entire financial year in the entire GST system for a taxpayer.
12. What will be the validity of the E invoice generated on the portal?
- As clarified, E invoice will not be generated at the GST Portal. It will be generated only at the suppliers billing software.
- It will be uploaded into GTSR 1 only once it has been validated and registered by the invoice registration system.
- After it has been validated and is available in GSTR 1, it will be visible to the counterparty in his GSTR 2A.
- Thereafter it will be visible and available for the entire financial year.
- As far as data on IRP is concerned, it will be available for 24 hours only.
13. Will the E invoice schema cater to the reverse charge mechanism (RCM)?
Yes, E invoice schema contains a reverse charge mechanism as well.
14. Will there be an option for linking multiple invoices in case of debit/credit note?
Yes, it will be allowed to link credit/debit notes.
15. Whether exports would require E invoice compliance? Also, does it allow the declaration of export invoices/zero rated supplies?
Answer to both the questions is Yes, E invoice schema also caters export invoices and declaration as well.









