Who is required to make an E-way bill in GST? procedure and liability
Table of Contents
Introduction
E – waybill is a document required for the movement of Goods. It is not always related to the sale or supply. But if there is a movement, E waybill should be prepared. It is covered by GST provisions. It contains information related to the goods. Any mismatch in the data given in E waybill and actual goods can lead to confiscation of Goods. The items confiscated can be released on payment of penalty. But if the penalty is not paid, they can be sold to recover the dues.
Liability to raise an E waybill
When Should eWay Bill be issued?
E-Way bill has to be generated whenever there is a movement of goods in a vehicle/or by any other motorized mode, of value more than Rs. 50,000 (either single Invoice or in aggregate of all invoices to the same recipient ) –
- In relation to a ‘supply’
- For reasons other than a ‘supply’ ( say a return, shifting of stock from one place to another)
- Due to inward ‘supply’ from an unregistered person.
Related Topic:
Penalty of the 1000 rupees for minor mistakes in E-way bill
For certain specified Goods, the e-way bill needs to be generated mandatorily even if the value of the consignment of Goods is less than Rs. 50,000:
- Goods are sent by the registered Principal to an unregistered job worker to a different state.
- Inter-State movement of Handicraft goods by a dealer exempted from GST registration.
Related Topic:
NO TAX & PENALTY U/S 129 OF GST FOR NON-GENERATION OF E-WAY BILL
Who should Generate an E-Way Bill?
In a transaction mostly three persons are involved. The seller, receiver, and the transporter. They may all have different registration status. Any one of the three can generate an E-way bill according to the registration status of the person.
Registered Person – Whenever there is a movement of goods of more than Rs 50000/- in value to or from a registered person, E-way bill generation is mandatory. However, if the value of goods is less it can be generated voluntarily by the dealer or the transporter
Unregistered Persons – Unregistered persons are also required to generate an e-Way Bill with the help of Adhar and PAN number. However in case, the recipient is a registered person, the receiver will have to ensure all the compliances as if he was a registered supplier.
Transporter – Transporters carrying goods by road, air, rail, etc. also need to generate an e-Way Bill if the supplier has not generated an e-Way Bill. Unregistered Transporters will be issued Transporter ID on enrolling on the e-way bill portal after which Eway bills can be generated.
A composite dealer can also issue an E-way bill but only for intrastate supply.
Related Topic:
E-Way bill — Flowchart & amp and salient features
Unregistered consumer-In cases where goods whose value exceeds Rs. 50,000 is transported by a consumer’s own vehicle (assuming the recipient consumer is unregistered), he has to carry an e-way bill during the transportation of such goods. The consumer can fill in the vehicle number in Part B of Form GST EWB-01. If the person transporting the goods is an unregistered person or a normal citizen, he can either request the supplier to generate an e-way bill or he can generate it himself by logging into the e-way bill portal for citizens.
In cases where Principal supply is supply of services – Where the Principal supply is supply of services, EWB is not required to be generated. However, in cases where along with Supply of services, movement of goods are also involved (For example – printing services, catering services, pandal or shamiana services, works contract services, Etc. ) in such cases EWB may be required to be generated.
EWB may be generated by entering the details of HSN code of the goods, along with SAC (Service Accounting Code) of services involved.
| Situation | Who should generate the bill? |
| The supplier is carrying the goods in his/her own vehicle |
Supplier |
| Supplier (Registered) hands over the goods to a transporter |
Supplier or Transporter (when not generated by the supplier) |
| Supplier (unregistered) hands over the goods to a transporter |
Transporter |
| Goods are transported by the recipient in a hired vehicle |
Recipient |
| Goods are transported by the supplier in a hired vehicle |
Supplier |
| Goods are transported by the recipient in his own vehicle |
Recipient |
Related Topic:
Download latest user manual of e-way bill
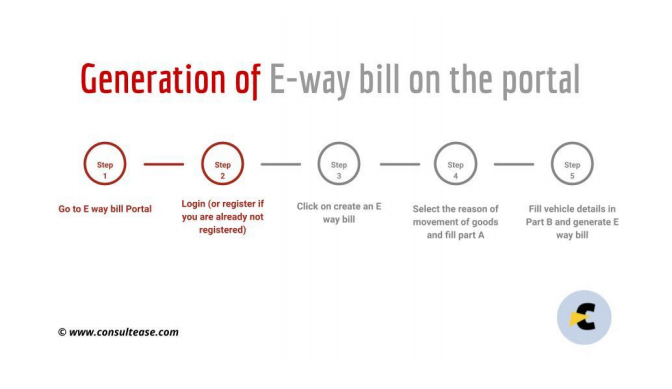
How to make an E waybill?
There are some requirements to be fulfilled before generating an E waybill
- The person has to be registered on the EWB portal.
- The Invoice/ Bill/ Challan related to the consignment of goods must be present.
- If transport is by road – Transporter ID or the Vehicle number.
- If transport is by rail, air, or ship – Transporter ID, Transport document number, and date on the document.( It can also be filled later by the transporter)
What information is required in an E waybill?
We are giving you the procedure assuming that the registered dealer (supplier) is making an interstate sale. The name and address of the supplier will be auto-populated.
a. He has to enter the GSTIN of the Recipient. The portal will auto-populate the name and address of the receiver.
b. Normally the goods will be sent to the registered address of the buyer. But there is a facility by which the goods will be billed to the registered address but transported to any other address as per the wishes of the buyer. GST will be levied as per the registered address only. The Registered Address of the buyer will be deemed to be the place of supply.
BILL TO SHIP TO
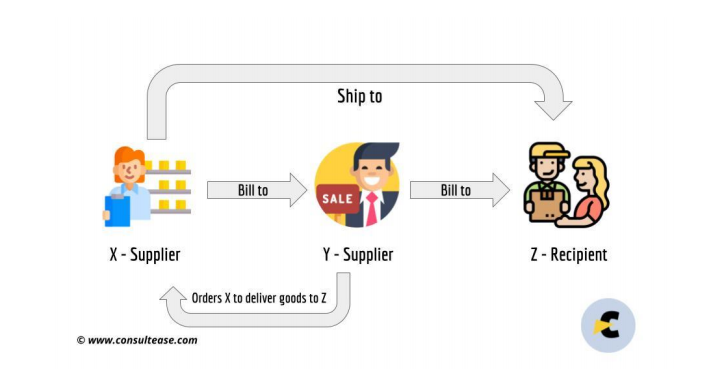
There is an option of “BILL TO SHIP TO”. If he has to send goods to any place other than the registered place of business of the receiver then he can use that option. The invoice will be issued always on the basis of the registered place of business of the recipient. But an E-way bill can be issued for the place the goods have to be actually transported.
c) Enter the correct address of the place where goods have to be sent. The portal will show the approximate distance the goods have to travel.
d)Then enter the brief description of the goods according to the following items.
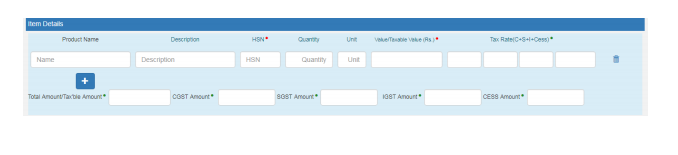
e) Item Details: Add the details of the consignment (HSN code-wise) in this section:
- Product name
- Description
- HSN Code
- Quantity,
- Unit,
- Value/Taxable value
- Tax rates of CGST and SGST or IGST (in %)
- Tax rate of Cess, if any charged (in %)
Note- 1)The amount of tax will be auto-populated.
2) If there is any service then do not enter any quantity
3) For the generation of the E-way bill at least one of the supplies has to be goods. If all the entries will be of service, then E -way bill will not be generated.
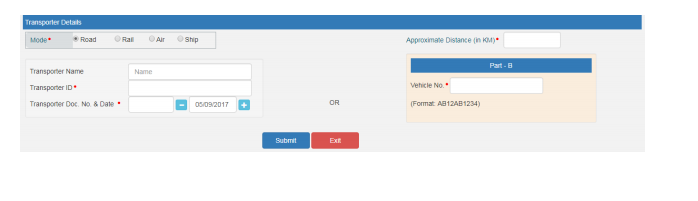
f) Transporter details: The mode of transport(road/rail/ship/air) and the approximate distance covered (in KM) needs to be compulsorily mentioned in this part. Apart from the above, either of the details can be mentioned:
- Transporter name, transporter ID, transporter Doc. No. & Date.
OR
- Vehicle number in which consignment is being transported.
Click on ‘Submit’. The system validates data entered and throws up an error if any.
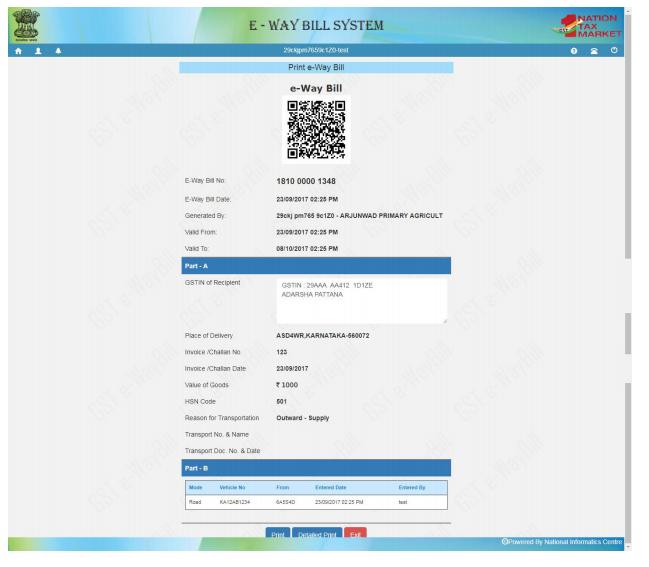
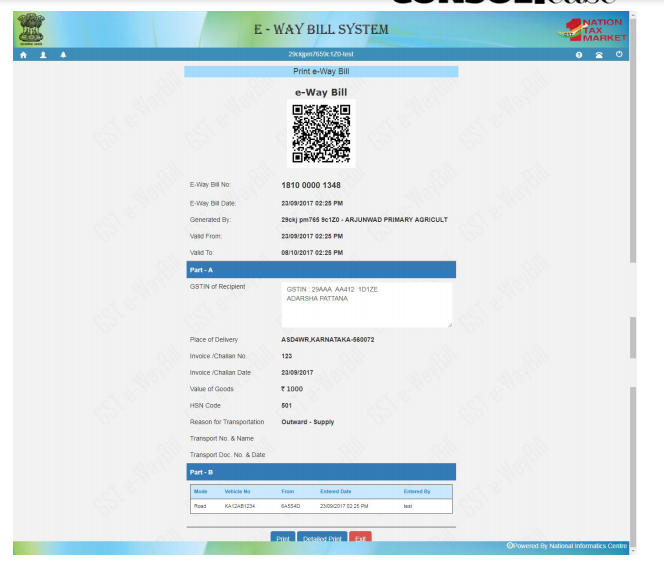
If there is no error then your request is processed and the E-way bill in Form EWB-01 with a unique 12 digit number is generated. The E-way bill generated looks like this:
Print and carry the e-way bill for transporting the goods in the selected mode of transport and the selected conveyance.
You can print the e-way bill anytime as follows:
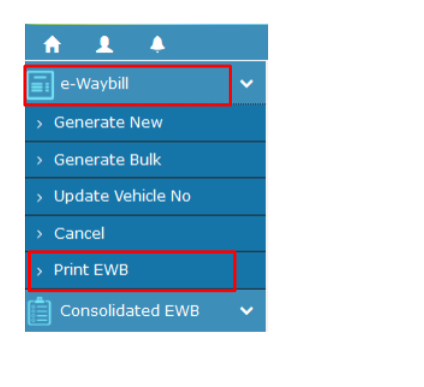
Step-1: Click on the ‘Print EWB’ sub-option under the ‘E-waybill option
Step-2: Enter the relevant E-way bill number -12 digit number and click on ‘Go’
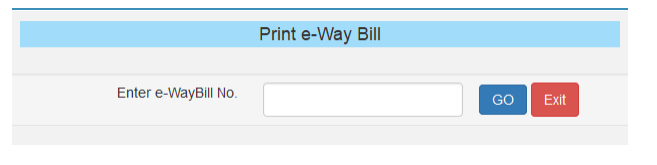
Step-3: Click on the ‘Print’ or ‘detailed print’ button on the EWB that appears:
E way bill Blockage
GSTR 1 return is for reporting of outward sales made during the taxable period. GSTR 3B return is for claiming and adjustment of the input tax credit and payment of the balance output tax. Hence the government receives revenue only when the dealer files his 3B return. It came to the notice that many taxpayers were filing GSTR 1 to show the invoices in 2A of their customers but were not filing 3B returns to avoid payment of tax. According to the GST act, ITC can only be claimed by the buyer when it has been paid by the seller. The non-filing of 3B will disable the buyer from claiming and availing the ITC for which they have already paid. Therefore to control such a menace the government brought rules 138E(a) and (b) of CGST Rules 2017.
According to these rules;
The E-Way bill generation facility of a taxpayer will be restricted if
- The taxpayer fails to file their form GSTR 3B returns or
- Statement in form GST CMP-08
For two or more consecutive taxable periods.
It means that if monthly 3B filers did not file their returns consecutively for two months or more,or quarterly 3B filers did not file their returns consecutively for two quarters or more, then their E- way bill generation facility will be withdrawn. Now they will not be able to make any single sale above Rs 50000 or any interstate sale.
How to unblock E waybill?
1)Filing of GSTR-3
When the defaulting taxpayer files the form 3B return for the defaulting period, his GSTIN will get unblocked automatically by the next day. A taxpayer can also generate the e-way bill soon after filing his returns by following the steps below :
- Visit the EWB portal and choose the option ‘Search Update Block Status’.
- Enter the GSTIN, CAPTCHA Code, and click on ‘Go’.
- Click on ‘Update Unblock Status from GST Common Portal’; this will reflect the recent filing status.
- In case this doesn’t work, a taxpayer can reach out to the GST Help Desk and get the query resolved.
2)Unblocking through online application in EWB-05
If the defaulting taxpayer has sufficient cause for non-filing of GSTR 3B, then he can file an application in form EWB-05 . Such a request cannot be rejected without giving an adequate opportunity to be heard.
What are the consequences of not making an E waybill?
The dealer would be unable to send/receive goods without an E-way bill. If he transports goods without E- way bill then he may have to face a fine equivalent to the output tax. His goods could be detained/ seized and then would be released only after payment of tax and penalty. His whole business will come to a halt. He has to face the anger of his customers as well. Thus it is better to become compliant than facing such hardships. Even a transporter or registered recipient can not generate E way bill for that sale. The seller also cannot work as an unregistered dealer.
E-way bills once generated are good enough for transport even if the GSTIN of the supplier has been blocked.

 ConsultEase Administrator
ConsultEase Administrator
Consultant
Faridabad, India
As a Consultease Administrator, I'm responsible for the smooth administration of our portal. Reach out to me in case you need help.








