How to File the Income Tax Return of a Salaried Person in 2021
If you are working in the Private or the Public sector & your total income exceeds the exemption limit, you must file your income tax returns. For an employee, their main source of income is via salary. Such employees need to file their Income-tax return in the FORM ITR – 1 SAHAJ
This article explains how salaried person should prepare their income tax return in 2021. In this post, we will try to understand what needs to be done before filing your income tax return and how to file the Income Tax Return in 2021
Table of Contents
ITR – 1
FORM ITR-1 popularly known as Income tax Sahaj is filed by residents (other than Not Ordinarily Resident) taxpayers having total income up to Rs. 50 Lakhs having Income from Salaries, Other Sources(interest, pension, dividend, etc.) & agricultural income up to Rs. 5,000. There are various ITR forms on the E-filing portal based on the source of income of a person. Therefore, a person should furnish their return as per the source of their Income.
Eligibility to File ITR form 1
ITR-1 is applicable on a Resident(other than Not Ordinarily Resident) Individual having total Income up to Rs. 50 Lakhs from the following sources:
Income from –
-
- Salary
- One house property
- other sources(excluding Income from lottery & racehorses)
In case, where the Income of a spouse or minor child is clubbed in the income of the assessee limitation on income specified above should be followed.
Related Topic:
Calculation Of Income Tax And Filing Of ITR On Income Tax Portal
Who cannot file ITR form – 1
- Form ITR -1 cannot be furnished by a person fulfilling the following conditions –
- The assessee is a Director in a company or has held any unlisted equity share in the previous year.
- The assessee has earned income from the following sources:
- More than one House property
- Legal gambling, racehorses, lottery, etc.
- Taxable short/long term capital gains
- Agricultural income of more than Rs. 5000
- Profits and Gains of Business or Profession
- have any asset or financial interest in any entity or income from sources, which are located outside India.
- The assessee has signing authority in any account which is located outside India
- the assessee who has cash withdrawals of more than Rs. 1 crore & tax has been deducted u/s 194N
- In the case of an individual where payment or deduction of tax has been deferred on ESOP.
- who has any losses in the previous year which is to be brought forward or to be carried forward under any head of income
- Individual claiming relief under section 90/90A/91 i.e. relief of foreign tax paid or double taxation.
Related Topic:
15 Reasons Why We Should File an ITR
FORM-16
Form 16 is a Certificate issued to salaried individuals by their employers, in which the employer is certifying the details of your salary earned & TDS deducted during the year. While furnishing ITR you may require your FORM 16 as it contains the information regarding your salary such as the breakup of your salary, deductions, TDS, etc.
This certificate has two parts –
- Part A: This part has information of Employer & employee such as name & address PAN & TAN no. period of employment, TDS deducted & deposited with the government.
- Part B: includes the details of Salary paid, Deductions allowed, any other income tax payable, etc.
You will have to ask your employer for FORM-16, If you have left your job & you are working under a new employer you can ask both of your employers for Form 16.
Related Topic:
Which Income Tax Return Form You Should File
Check the bank statements for incomes skipped in Form 16
Incomes like interest may get skipped in Form 16. Therefore, you will need to check your bank statements while furnishing your ITR-1. As you will have to declare all the income receipts credited in your bank account in the relevant heads of Income.
Related Topic:
Income Tax Deductions – Individuals and HUF (FY 2019-20)
Some Important deductions
- Section 80(C) – Deductions on Investments
It is the most popular & beneficial deduction as it promotes Investment among the taxpayers. A taxpayer can reduce their taxable income by making investments in these tax-saving investments & incurring eligible expenses
This Section Includes subsections, 80CCC ( Insurance Premium ), 80CCD ( Pension Contribution )
The maximum deduction allowed in this section is Rs. 1,50,000
Few eligible investments under this section –
- Tax saving FD
- Sukanya samridhi scheme
- NPS scheme
Related Topic:
DIY: How to file TDS return without the help of any expert/software
- Section 80GG – House rent paid
This deduction is allowed on rent paid by the taxpayer if HRA is not received. The taxpayer ( also Spouse & minor child ) should not own residential property at the place of employment also the taxpayer must be living on rent & paying it and he must not have any residential self-occupied property in any other place.
Deduction available is the least of the following:
- Rent paid minus 10% of adjusted total income
- Rs 5,000/- per month
- 25% of adjusted total income
- Section 80TTA – Interest received on Savings account
Deduction of interest up to Rs. 10000. Interest should be from a Savings account with a bank, cooperative society, or post office.
- Section 80D – Medical Insurance
An individual can claim a deduction on the premium paid for Medical insurance.
| Self, Spouse & dependent children | Under 60 Years | Up to 25000 |
| Parents | Under 60 Years | Up to 25000 |
| Self, Spouse & dependent children | 60 years or above | Up to 50000 |
| Parents | 60 years or above | Up to 50000 |
It means that if both taxpayer & his parents are senior citizens he can claim a deduction up to Rs 1,00,000 under this section. Also, an additional deduction of Rs. 5,000 for preventive health checks.
Step by step guide to File ITR – 1
Step 1: Visit https://wwwdotincometaxdotgovdotin/
Step 2: Click on Login
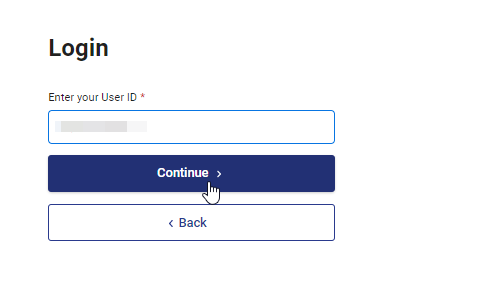
Step 3: Enter your User ID (pan/aadhar) & click on Continue
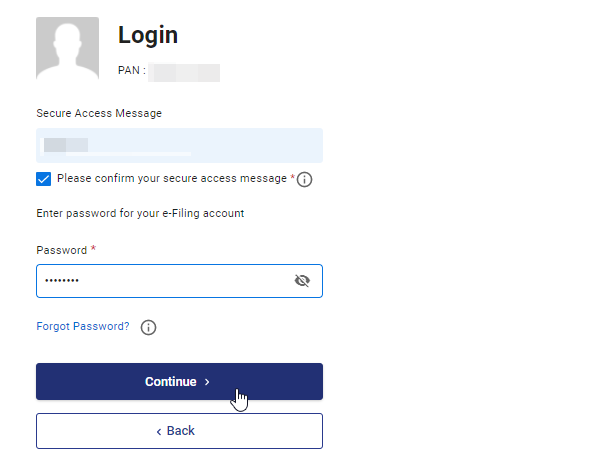
Step 4: Enter your password & Login
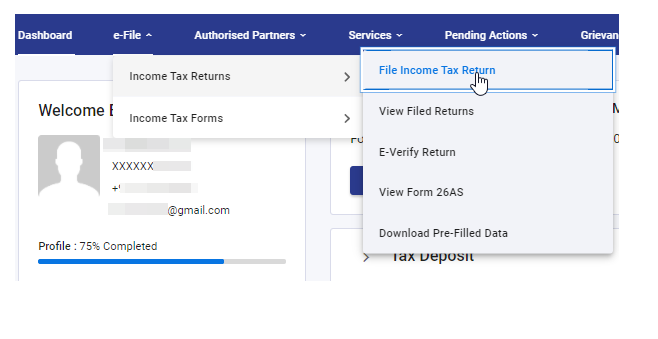
Step 5: Go to E-file tab > income tax returns > File income tax return
Step 6: then
> select Assessment year
> Select mode of Filing – Online
> Select status – individual
> Select ITR form – ITR-1
> then Click on Proceed with ITR-1
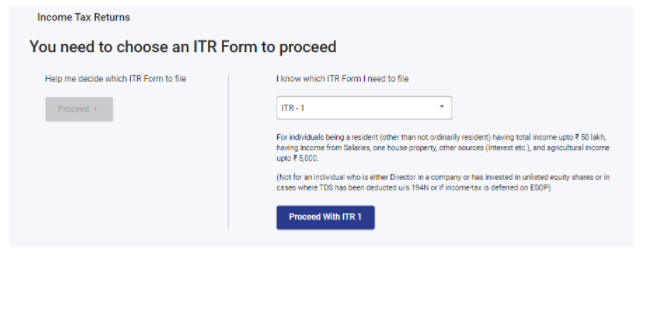
Step 7: Select the reason for filing the Income-tax return, then click on Continue.
Step 8: On the next screen, Return Summary with pre-filled data will be displayed.
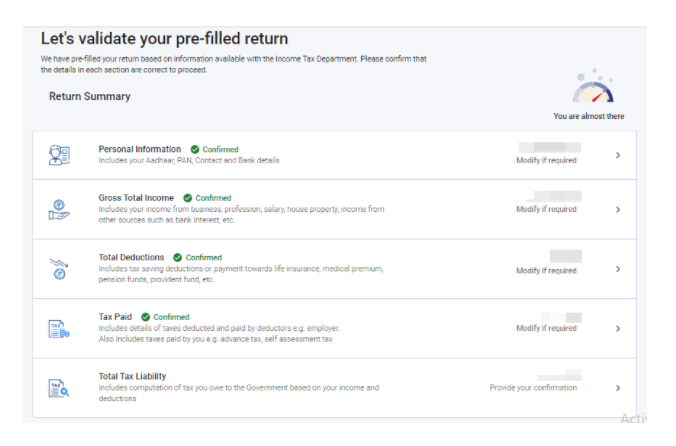
Step 9: Verify your personal information – You just have to verify the pre-filled information & make changes if required. Also, you will have to provide the following information by selecting appropriate options.
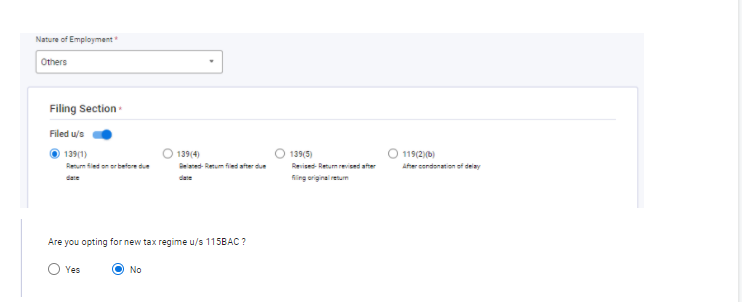
- Nature of Employment
- Filing Section
- Whether you want to Opt for the new tax regime U/s 115BAC or you want to stay in the Old tax regime.
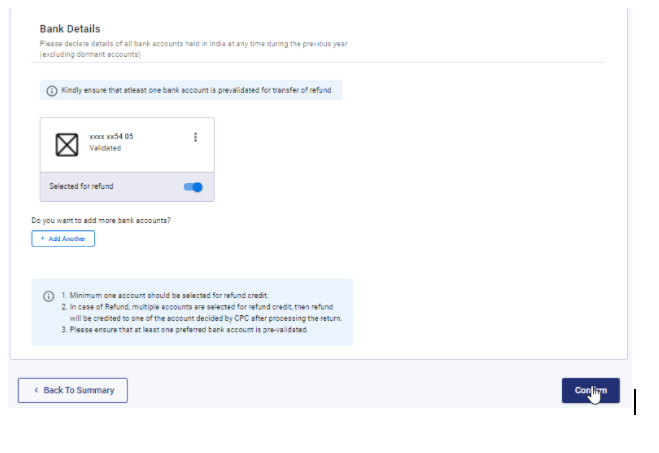
- Select any one pre-validated bank or add any new bank account details in which you refund
Answer all these questions & then proceed to the next page.
Step 10: Gross total income – Assessee will have to calculate his gross total income from the five heads & disclose his exempt incomes
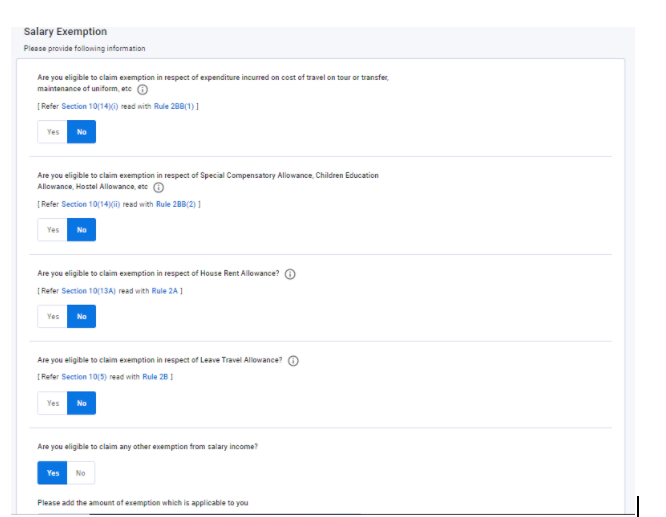
- First, select if you are eligible to Claim Exemption in respect of
- expenditure incurred on the cost of travel on tour or transfer, maintenance of uniform, etc [section 10(14)(i)]
- Special Compensatory Allowance, Children Education Allowance, Hostel Allowance, etc [Section-10(14)(ii)]
- House Rent Allowance [Section-10(13A)]
- Leave Travel Allowance [Section-10(5)]
- Any other Exemption as specified there
Then, Enter your gross salary, Income from house property if earned & Income from other sources ( Interest, Pension, Dividend, etc.)
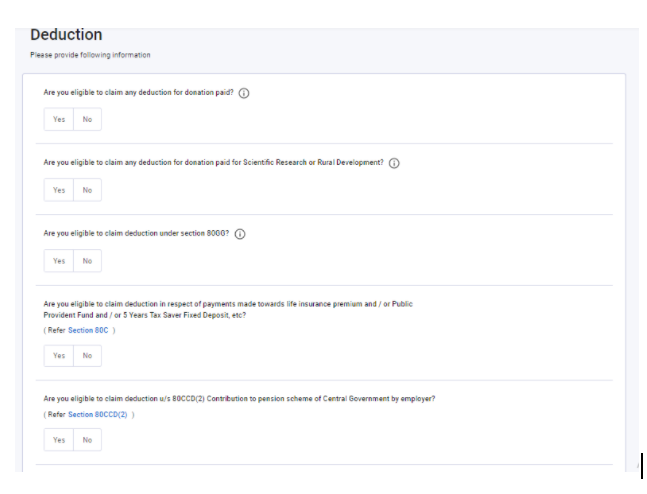
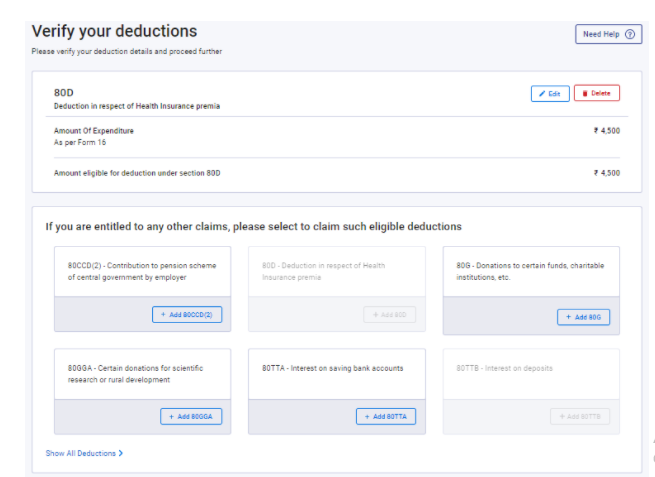
Step 10: Total Deductions – Details of Tax savings Deductions, Expenses Incurred by Assessee during the Previous year which are eligible for deduction.
Opt for any deduction that you are eligible for, such as –
- Life insurance premium and/or Public Provident Fund and/or 5 Years Tax Saver Fixed Deposit, etc [Section 80C]
- medical insurance premium and/or preventive health check-up and/or medical expenditure [Section 80D]
- deduction in respect of payment made towards interest on loan taken for higher education for self and relative [Section 80E]
- Many more Deductions as specified in the Provisions of the Income-tax act
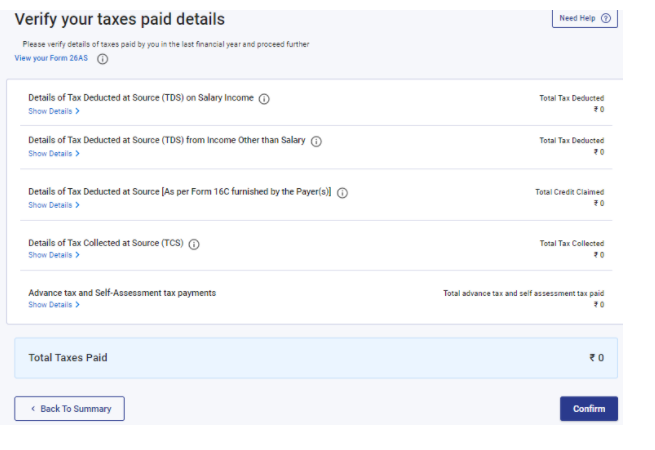
Step 10: Tax Paid – It includes Details of tax deducted & paid by deductors, also tax paid by the assessee himself e.g. advance tax, self-assessment tax.
Step 11: Total tax Liability – It includes details of tax to be paid to the government based on our income & deductions. If you any relief under Section 89 then Enter its amount. Also, you will have to file Form 10E. After verifying the amount click on Confirm.
Step 12: In the next screen it will show the total amount Payable
Step 13: Now validate the return Enter the required details & select whether you are furnishing the return in your Capacity as self or as a representative.
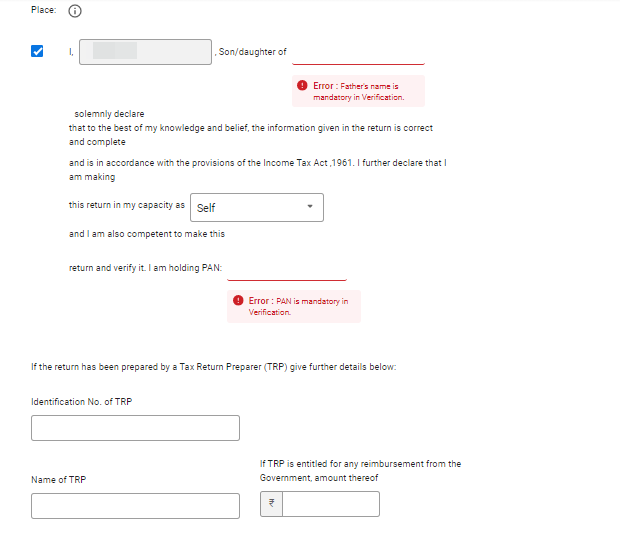
Step 14: Verify your return summary, Check all the details & make sure everything is correct, or else go back and edit the part of the form which requires correction. Proceed to Validation
Step 15: On the next screen it will show if there is any error or omission in the Form. Correct those errors
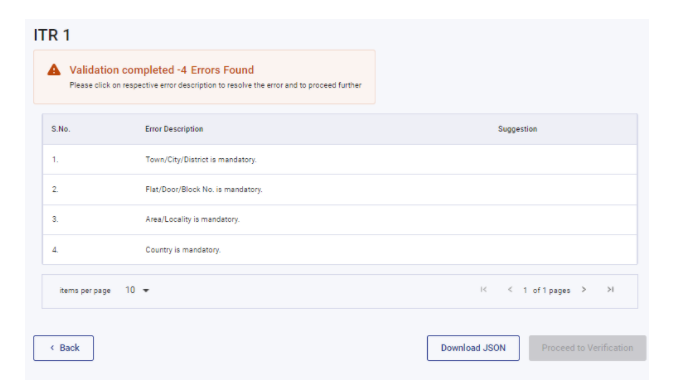
After correcting all the errors it will show that “Validation successful > “no errors were found”
then, click on Proceed to Verification.
Related Topic:
CTC – Understand What Is Cost to Company and How to Calculate It?
Step 16: You can submit the return, verify it later or you can E-verify it through Aadhar OTP or OTP from a Pre-validated bank account.
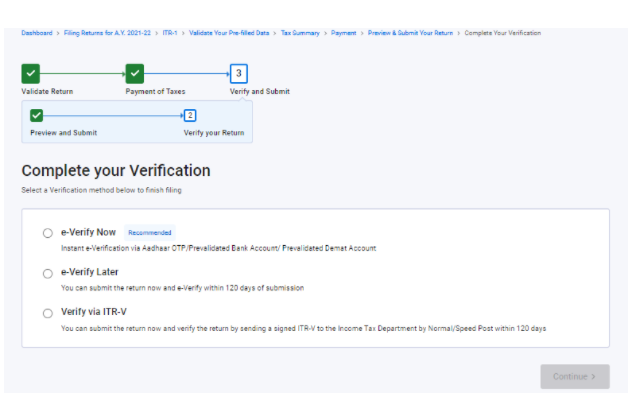 Conclusion:
Conclusion:
If you’re a salaried employee then it is important to file your income tax return on time. You must have received a lot of information about how to do this. It will be worth the effort because if you don’t file your taxes correctly or on time then you will have to penalty for late filing. We also offer an Advance Income Tax Certificate Course that teaches all aspects of Indian income tax law and helps you to gain advanced knowledge regarding Income Tax. Contact us today at info@consultease.com or call +91 962-574-0572 to learn more about our course options and schedule availability.
 ConsultEase Administrator
ConsultEase Administrator
Consultant
Faridabad, India
As a Consultease Administrator, I'm responsible for the smooth administration of our portal. Reach out to me in case you need help.








