Implementation of Labour Codes
Table of Contents
Why New Labour Codes
Economic Survey – States (Like Rajasthan from 2015) which are more flexible with Labour Laws are 25% more productive than their Counterparts
1. Only 10% of Entire Businesses in the Country is Organized
2. They are burdened with Compliance with almost 40 Central Labour Laws and 100 State Labour Laws
3. Labour Code looks to –
A. Simplify Labour Regulations
B. Balance between Employment Growth and Protection of Employee Rights
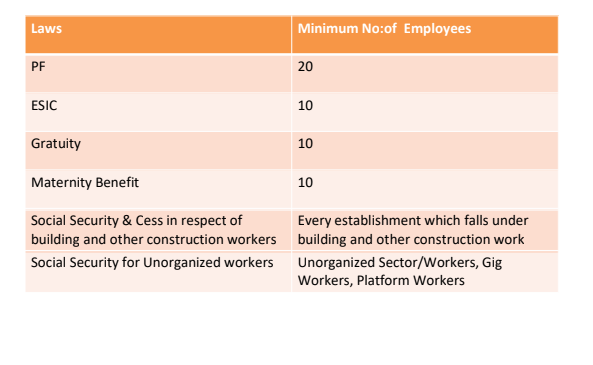
Employers Requirement –
1. Centralized Registration
2. Relief from Inspector Raj
3. Flexibility
Employees Requirement –
1. Inspector’s Duty Compromised
2. Labour Dept. Capability to implement
Government’s Requirement –
1. Help Employers hire more
2. Cover more workforce – Unorganized workforce
3. EODB for Foreign Investors
New Labour Codes – Principles for Governance
1. These Laws prescribe the ‘bare minimum
2. Contract Vs Status
3. Welfare Statutes interpreted with Equity & in view of principles of Justice
4. Acts not subsumed-
- Professional Tax Acts of States
- Shops & Establishments Acts
- Specialized PF Laws for seamen and workers in coal mines
- Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace
- Apprentices Act
- Bonded Labour Act
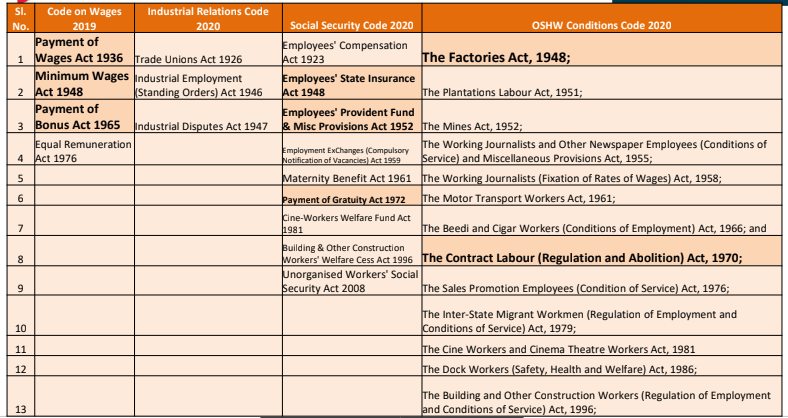
New Codes
1. The Code on Wages – Consolidating 4 Laws – Gazetted 8/8/2019
2. The Industrial Relations Code – Consolidating 3 Laws – Gazetted 29/9/2020
3. The Code on Social Security – Consolidating 9 Laws – Gazetted 29/9/2020
4. The Occupational Safety, health, and working Conditions Code – Consolidating 13 Laws – Gazetted 29/9/2020
They will become effective on the date notified – Possibly October 2021
Rule-making provision has been considerably widened. Hence many provisions which were in the Act will now be governed through Rules
Applicability
Definition of Wages
Wages have been defined u/s 2y of The Wage Code as –
– Inclusions – Basic, Dearness Allowance & Retaining allowance
– Exclusions – Bonus, House accommodation, PF (plus Interest), Conveyance Allowance, HRA, Sum paid, Award, Overtime, Commission
– Additional – Gratuity & retrenchment
Provision – Exclusions should be maximum of 50%
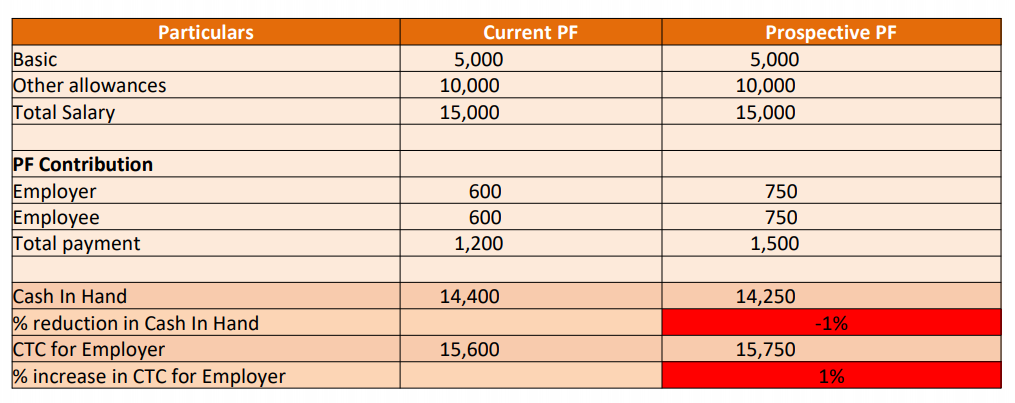
Explanation – Payment in kind up to 15% of “Total Wages” shall be deemed to be part of Wages As per Social Security Code, PF Deduction to be 10% and not 12% Gender Equality finds a place
For 3 months Central Govt can reduce employees’/employers’ contribution to PF/ESI in case of Pandemic/ Endemic/ Natural disasters
Other Issues in Salary –
1. Cash in hand of employees may go down but CTC for employers may go up
2. Retirement benefits will certainly increase
3. The gratuity will also go up if there is any change in basic wage.
Organizations have to pay gratuity as an amount equaling 15 days of last drawn basic wage for each year of service. So, an increase in basic wage will result in an increase in gratuity paid.
4. Those in a higher salary bracket will pay more tax as the tax planning option would be limited to 50% of the cost to the company (CTC). For E.g. tax deductions for HRA may go down
5. Scope of Minimum Wages rationalized – “Floor Wages” will be declared by Central Govt and State Govt cannot go below that
Wage Code: Changes
1. Definition of Establishment covers ‘any place’ where any business/occupation is carried on.
Sec 2m – Establishment Any place from where any industry, trade, business, manufacture or occupation is carried on and includes Govt establishment
2. Appropriate Govt – Sec 2(d)-
A. For Central Govt undertakings & PSUs – Central Govt.
B. For other Undertakings registered in 1 State – State Govt
C. For Multi-State Registered Undertakings – Central Govt.
3. Sec 4B: Deductions Sec 18(3) –
A. Cannot be more than 50% of the total Wages
4. Minimum Rate – Sec 6 & Sec 9 –
A. Central Govt will notify “Floor Rate”
B. State Govt can go above Floor Rate
5. Overtime Rate (Sec 14 & 13) –
A. Double the normal rate
B. However, there should be an off day for every 7 day period
6. Employee (Sec 2k) – means –
A. Other than Apprentice
B. Employed to do Skilled, semi-skilled, unskilled job
C. Any type of Work including managerial or administrative
7. Worker (Sec 2z) – means –
A. Other than Apprentice
B. Employed to do Skilled, semi-skilled, unskilled job
C. Technical, operational, supervisory or clerical job
D. Not doing the managerial or administrative job
E. Doing Supervisory job and not drawing more than Rs.15000 per month
8. Employer includes –
A. Manager of a factory
B. A person who has ultimate control like MD
C. Contractor
D. Legal representative of a deceased employer
Read & download a full copy in pdf:









