Science of Enhancing Quality of Audit And Assurance Service by CA
Table of Contents
Science of Enhancing Quality of Audit And Assurance Service by CA
History of Audit
- The word Audit is derived from a Latin word ‘Audrie’ which means to ‘hear’.
- During the medieval times when manual bookkeeping was prevalent, auditors in Britain used to hear the accounts read out for them and checked that the organization’s personnel were not negligent or fake.
- Therefore, the concept of Audit came in prevalence.
- An Audit is an objective inspection & evaluation of the financial statements of an organization to make sure that the records are a fair and accurate representation of the transactions they claim to represent.
- It can be done internally by employees of the organization, or externally by an outside firm.
How Does Audit Help?
• Audit helps in:
1.) Maintaining an effective system
2.) Achieving Company’s Goals
3.) Preventing fraud
4.) Minimize the cost of capital
Audit Evidence, Audit Report, And Assurance Report
• Auditing Evidence is the information collected for the review of a company’s Financial Transactions and internal control practices and other factors necessary for the certification of financial statements by an auditor or certified public accountant.
• An Audit Report is a written opinion of an auditor regarding an entity’s financial statement.
• Assurance Report: The ISRE (International Standard On Review Engagement) say’s that the review report should contain a clear written concept of negative assurance. Based on the work performed, the auditor should assess whether any information obtained during the review indicates that the financial statement does not give a true and fair view in accordance with the identified financial reporting framework.
Stages of External Audit Work
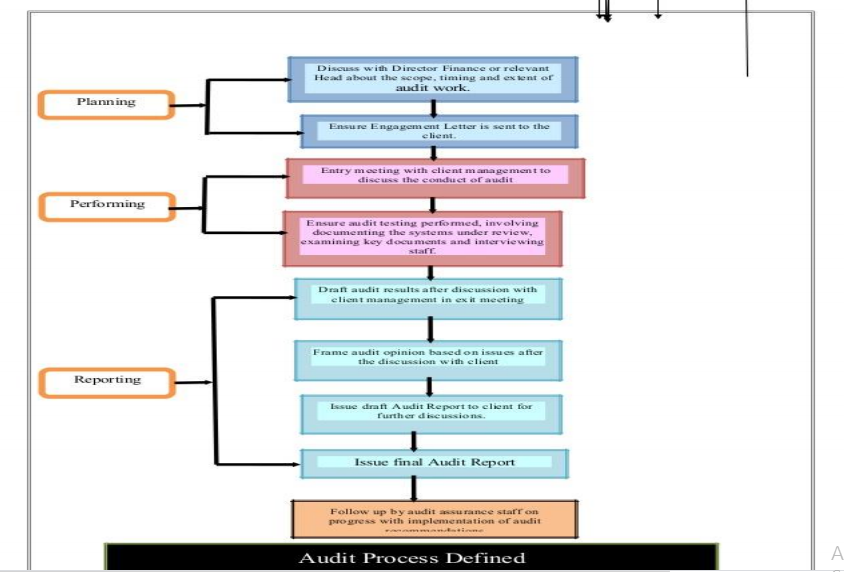
Role And Responsibility of An Auditor
Role of Auditors:
- International Audit Standards maintain that an auditor’s mandate may require him to take cognizance and report matters that come to his knowledge in performing his audit duties which relate to:
A. Compliance with legislative or regulatory requirements;
B. Adequacy of accounting and control systems;
C. Viability of economic activities, programs, and projects
- Responsibilities are:
A. Prepare an Audit Report.
B. Form a negative opinion, where necessary
C. Comply with Auditing Standards
D. Make inquiries
E. Reporting of fraud
F. Adhere to the Code of Ethics and Code of Professional Conduct
G. Lend assistance in case of a branch audit
Expectation Gap
- The gap between the expectation of the users of the Assurance report and the firm’s responsibilities in respect of those reports is called the expectation gap.
- Some misunderstandings of users:
A.) Holding auditors solely liable for the preparation of the financial statements.
B.) A little perception of the concept of materiality.
C.) Taking Reasonable Assurance as Absolute Assurance.
- This Gap can be reduced by:
A.) Expanding the Audit Report.
B.) Engagement Letter.
C.) Audit Committee
Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002
- In response to several accounting-related corporate scandals, Congress passed the above-mentioned act.
- The Act’s major provisions includes:
A.) The requirement of CEO/CFO certification of Financial Statements.
B.) The requirement of an Auditor examination of the company’s internal control.
C.) Creation of Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (PCAOB) to serve as an auditing profession “Watchdog”.
D.) Prohibition of certain client services by firms conducting a client’s audit.
Read & Download the full copy in pdf:
 CA Rajkumar Adukia
CA Rajkumar Adukia
CA (Dr.) Adukia left no stone unturned during his career span expanding to more than 37 years. He is chairman of Meridian Business Consultants Private Limited. The company is involved in providing A to Z services required by any business. CA (Dr.) Adukia is a legendary example of seeking ways to explore new areas of business and profession. He is a pioneer of many areas of the practice which were never thought before by professionals. His mantra is to provide services to clients that help them in building better and sustainable businesses. He is a knowledge seeker and believes that knowledge needs to be ingrained and used for the benefit of society at large. He strongly believes that professionals have to go beyond the traditional areas of practice like audit and direct and indirect taxation. These are the least rewarded areas in comparison to the knowledge and expertise we have as chartered accountants. He feels that one must expand himself to serve better and not settle for less whether in terms of rewards or the various kinds of assignments. Being an adherent follower of the “Science of Getting Rich, he believes the pie gets bigger and bigger so that it can cater to every individual’s needs. We contribute to creating an abundant universe by asking for more riches. And he desires better remuneration for assignments not just for himself but for all his fellow professionals. He achieves this by mentoring the professionals, handholding them through various workshops, webinars, and lectures he conducts for professionals who wish to enter into new areas of practice. He has mentored 1000 professionals for passing the Insolvency Exam and Valuation Exam. Professional Areas of Expertise He has been a well know professional exhibiting expertise and providing services in the following areas: Taxation Corporate Advisory & Compliance Corporate Insolvency& Bankruptcy Civil And Commercial Litigation Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR) Intellectual Property Rights Anti-trust & Competition Real Estate Family Law Criminal Laws Labour &Employment Laws Banking & Finance Charitable Organizations Forensic Services Entertainment, Media & Broadcasting Pharmaceuticals, Food & Drug Antidumping, International Trade Law& WTO Telecommunication Information Technology Infrastructure Projects Insurance Law Cooperative Sector Environment Law He represents clients at Debt recovery tribunals and has filed applications under the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code 2016 for recovery of debts through the National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT). He has also represented clients at various commercial tribunals like The Appellate tribunal under The Prevention of Money Laundering Act 2002, The National Company Law Appellate Tribunal for cases under Companies Act 2013 and the Competition Act 2002, the Telecom Disputes Settlement and Appellate Tribunal for cases under the Information Technology Act 2000. Experience His vast experience includes training and professional services to banks, financial institutions, Corporate, Government Departments, and Regulators and as: An eminent Speaker and Business Advisor, An expert on Business laws, cyber laws, cybersecurity, International Forensic Expert Faculty at Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India Author of more than 300 books on a wide variety of topics ranging from those dealing with Trade, Taxation, Finance, Real Estate, the Insolvency & Bankruptcy Code, Intellectual Property Rights, Banking laws, Emerging technologies like AI and Blockchain to topics relating to personal and professional growth. He is the winner of National Book Honor Awards 2018 He has been conducting seminars and lectures across various countries. Authority on Banking Laws, Insolvency Laws, Insurance Laws, Intellectual property laws, Indian GAAP, IFRS, and Ind-AS. Business advisor for various companies on varied subjects Travelled across the globe for his professional work and knowledge sharing. He has widely travelled three fourth of globe addressing international conferences and seminar on various international issues like Corporate Social Responsibility, Corporate Governance, Business Ethics etc. Education Having graduated from Sydenham College of Commerce & Economics in 1980 as a 5th rank holder at Bombay University and he has also received a Gold Medal for highest marks in Accountancy & Auditing. He cleared the Chartered Accountancy Examination with 1st Rank in Intermediate and 6th Rank in Final. He also secured 3rd Rank in the Final Cost Accountancy Course. He has been awarded the G.P. Kapadia prize for the best student of the year 1981. He also holds a Degree in law, Ph.D. in Corporate Governance in Mutual Funds, MBA, Diploma in IFRS (UK), and Diploma in Labour law and Labour welfare, Diploma in IPR, Diploma in Criminology. He has done Master in Business Finance, a one-year post qualification course by ICAI. He has also done Certificate Courses conducted by ICAI on Arbitration Forensic Audit and Fraud prevention Concurrent Audit Significant Professional Achievements: He is a member of the International Bar Association. The International Bar Association, established in 1947, is the world's leading international organization of legal practitioners, bar associations, and law societies. The IBA influences the development of international law reform and shapes the future of the legal profession throughout the world. He served as President of GST Research foundation, a society registered under Societies Registration Act, 1860. He is the Chairman of Association of Indian Investors, a Section 8 Company wherein its main thrust is to educate the layman about the principles of a safe investment, the complexity of the capital market, changing rules of the market operations, designing and implementing effective Internal Financial Control the framework, the framework on enhancing the Cybersecurity of the organizations and implementation of ISO 27000 framework and provide Corporate Governance Services. He is also Vice President of All India Insolvency Professionals. All India Insolvency professionals is an organization providing services in the field of insolvency and bankruptcy, corporate restructuring, etc. The Organization is currently having 200 professionals all over India as its members. Current& Past Memberships: International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) Foundation SME Group Insol India National Committee for Regional Affairs. Membership of the following committees of International Bar Association Asia Pacific Regional Forum Forum for Barristers and Advocates Arbitration Committee Bar Issues Commission (BIC) Member of INSOL India CAG Advisory Committee Quality Review Board, Government of India Professional Service CA (Dr.). Adukia’s service and contribution to the profession Chairman of WIRC of ICAI in 1997-98 International Member of Professional Accountants in Business Committee (PAIB) of the International Federation of Accountants (IFAC)from 2001 to 2004 Member of Inspection Panel of Reserve Bank of India Member of J.J. Irani committee (which drafted Companies Bill 2008) Member of Secretarial Standards Board of ICSI Member of Working Group of Competition Commission of India, National Housing Bank, NABARD, RBI, CBI, etc. Independent Director of Mutual Fund Company and Asset Management Company. Worked closely with the Ministry of Corporate Affairs on the drafting of various enactments. Served as Independent Director of SBI Funds Management Private Limited and Bank of India asset management co. ltd Served as Independent director at ICAI accounting research foundation section 8 company Actively involved with ICAI as a Central Council Member during the period when the convergence to IFRS was conceptualized in India and has been instrumental in materializing the idea. Address to Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India Address to Institute of Chartered Accountants of India Address to Institute of Company Secretaries of India Address to Institute of Cost Accountants of India Address to Chamber of Indian Micro Small & Medium Enterprises Speaker in IIA’s 2013 International Conference in Orlando on Green Audit. Faculty at Indian Institute of Corporate Affairs for courses on Insolvency Laws and Corporate laws. Faculty Speaker in Workshop on Commodity Risk Management for Bankers organized by CAFRAL (Centre for Advanced Financial Research and Learning) Faculty at National Institute of Securities Management (NISM)and Indian Institute of Corporate Affairs (IICA) Addressed the Program for Principal Inspecting Officers & Inspecting Officers by Reserve Bank of India- Department of Non-Banking Supervision. Addressed the National apex Chamber of Commerce and State apex Chamber of Commerce including his address to ASSOCHAM, Confederation of Indian Industry (CII), Federation of Indian Chamber of Commerce and Industry (FICCI), and All India Manufacturers Organization (AIMO). Addressed the CBI officers, officers of Serious Fraud Investigation Office (SFIO), and various State Police Academies. Addressed the SCOPE- Standing Conference of Public Enterprises which is an apex professional organization representing the Central Government Public Enterprises. It has also some State Enterprises, Banks and other Institutions as its members. Addressed the National Academy of Audit and Accounts (NAAA) He has been a panel member at the following Arbitral Institutions/Forums: International Bar Association Bombay High Court Indian Council of Arbitration The International Centre of Alternate Dispute Resolution The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India Bombay stock exchange National stock exchange Western Region - Ministry of Corporate Affairs, Government of India South Eastern region - Ministry of Corporate Affairs, Government of India North Western Region - Ministry of Corporate Affairs, Government of India India International ADR Association International and Domestic Arbitration Centre India ASSOCHAM ICADR Mumbai Centre for International Arbitration Main Mediation Centre Maharashtra & Goa Airports Authority of India (AII) Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited (BSNL) Global Life and Business Transformation Guru CA (Dr.) Adukia is a motivational speaker, Growth Coach, and Life and business coach. He has done various Self developments from India and the USA. CA (Dr.) Adukia has done a graduate course from Landmark worldwide which is personal and professional growth, training, and development company focusing on people achieving success and fulfillment. His exposure to advanced programs and introduction to leadership programs has made him the most sought-after trainer in the areas of business development and personal development. He has been a trainer at many corporates which has resulted in positive and permanent shifts in the quality and life of people. He is an adherent follower of “Think and Grow Rich” by Napoleon Hill. He is also trained by the Bob Proctor series on “Thinking into results”. His experience from his international training has been penned down in his various books on self-development. Some of his books on Self-development are 1. Magical Formula for Success 2. Strike Gold 3. Reinvent your Mind 4. Self-Empowerment 5. Genius is Universal 6. How to be super successful professional 7. Hoe to be a super successful person 8. Zooming your business and profession 9. Time management 10. Stress management 11. Goal setting CA (Dr.) Adukia is very passionate about learning new things and believes self-improvement is a permanent process. His zeal is infectious to any person who meets him either for professional growth advice, business growth advice or for personal growth advice. CA (Dr.) Adukia has given solutions to growth for everyone. He has done courses on: Winner Time management Stress management He has mastered programs on: Siddha Samadhi Yoga Silva mind control Alternative therapy Think and Grow Rich Art of living Reiki Awards and Accolades He has been felicitated with awards like The Jeejeebhoy Cup for proficiency and character, State Trainer by the Indian Junior Chamber, “Rajasthan Shree” by Rajasthan Udgosh, a noted Social Organization of Rajasthan and Several other awards as a successful leader in various fields. National Book Honors Award 2018 CA (Dr.) Adukia continuously endeavors to help the clients achieve the desired results through customized and innovative solutions that involve focusing on exploring opportunities and leveraging them to enhance the growth and expansion of his clients. Sharing knowledge is enhancing knowledge. CA (Dr.) Adukia encourages the precise energies in research, training, seminars, and books writing in the field, the one has passion.








